Event-driven architecture
Event sourcing - is a pattern that uses an append-only event log to store the full history of actions taken on data in a domain.
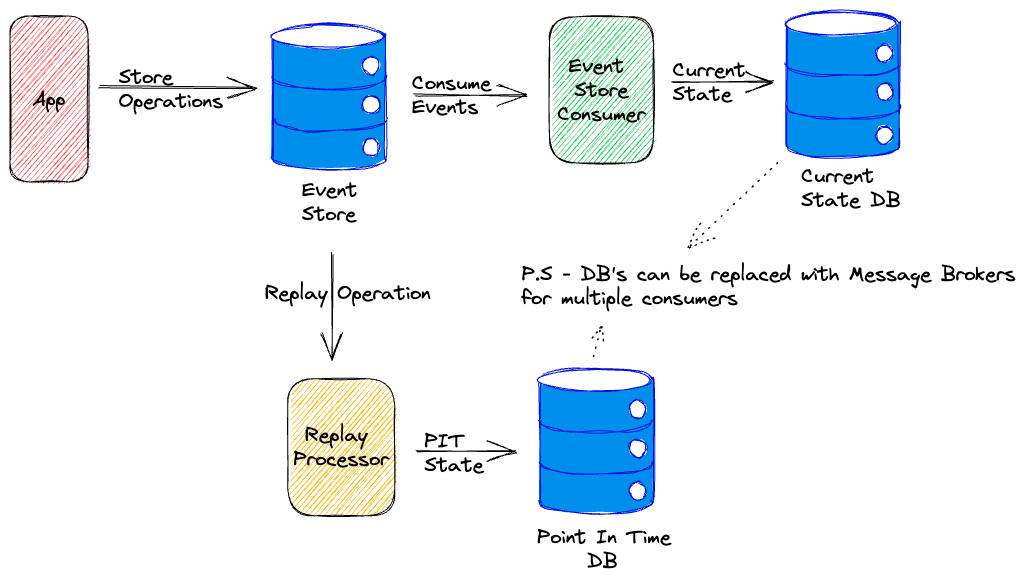
The application state is derived by replaying the events in the log.
This allows the state to be rebuilt at any point in time by replaying the events from the event log.
Common example of event sourcing is a Git.
Event - is a record of what happened in the domain, carries information about the state of the domain at the time of their occurrence.
Event is a subset of the message.
- Event don't have a destination.
- Event is a named fact that something has happened.
E.g: order created, order shipped, order cancelled.
Event log - is a sequence of events that happened in the domain.
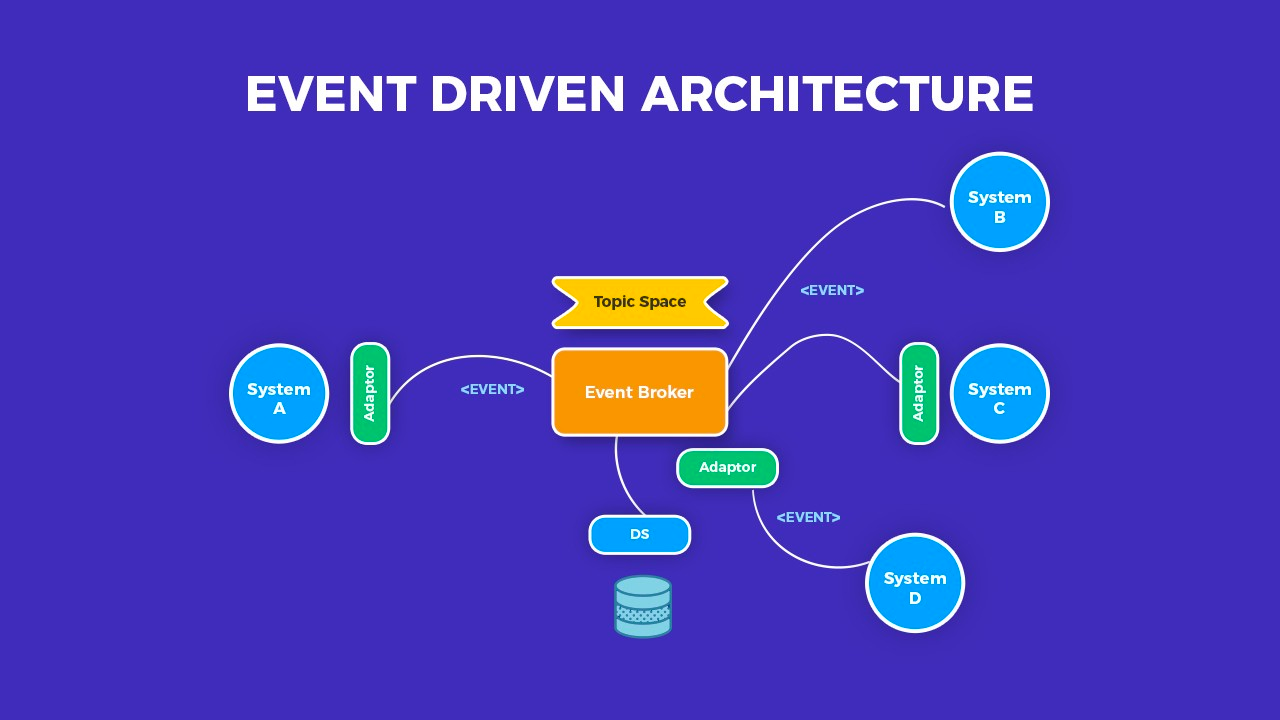
Event driven architecture - is a pattern that uses events to trigger and communicate between decoupled services.
Usually implemented using a message broker, such as Kafka or RabbitMQ.
- EDA is asynchronous, which means that the sender and receiver of the message don't need to interact instantly, events can be processed at a later time.
- We can have multiple consumers of the same event, each consumer can do something different with it. (pub/sub model)
- Easy to add new services, low coupling between services.
- High system reliability, because if one service is down, the event will be stored in the event log and will be processed later.
CQRS (Command Query Responsibility Segregation) - is a pattern that separates the read and write operations for a data store.
Different services can handle read and write operations separately.
Command - is an operation that changes the state of a system, checks its arguments, and enforces invariants.
imperative, e.g: create order, update order, delete order.
command -> change aggregate state -> event
Query - is a search/read operation that returns data from the system.
e.g: get order, get all orders.